一:分支结构
- 注意:Java分支语句的判断表达式里必须是布尔表达式,不像C/C++那么宽松
(1)if语句
A:基本语法
- 具体语法格式不再赘述,和C语言基本一致
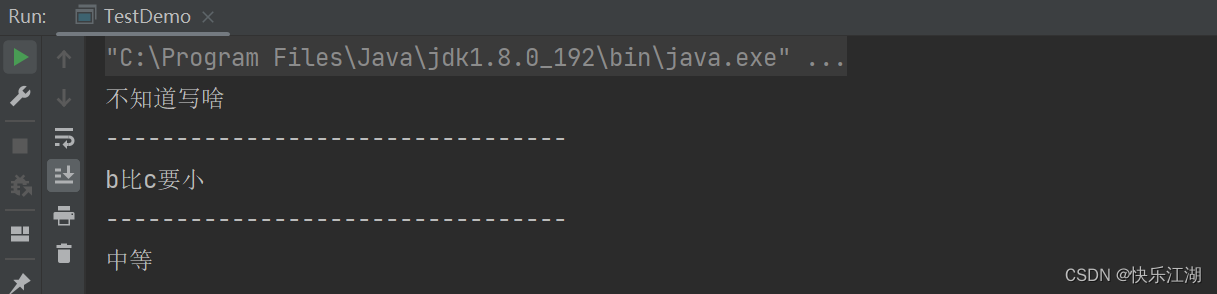
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//格式1
int a = 10;
if(a > 1){
System.out.println("不知道写啥");
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
//格式2
int b = 3;
int c = 5;
if(b > c){
System.out.println("b比c要大");
}else{
System.out.println("b比c要小");
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
//格式3
int score = 77;
if(score >= 90){
System.out.println("优秀");
}else if(score >= 80 && score < 90){
System.out.println("良好");
}else if(score >= 70 && score < 80){
System.out.println("中等");
}else if(score >= 60 && score < 70){
System.out.println("及格");
}else if(score >= 0 && score < 60){
System.out.println("不及格");
}else{
System.out.println("错误数据");
}
}
}
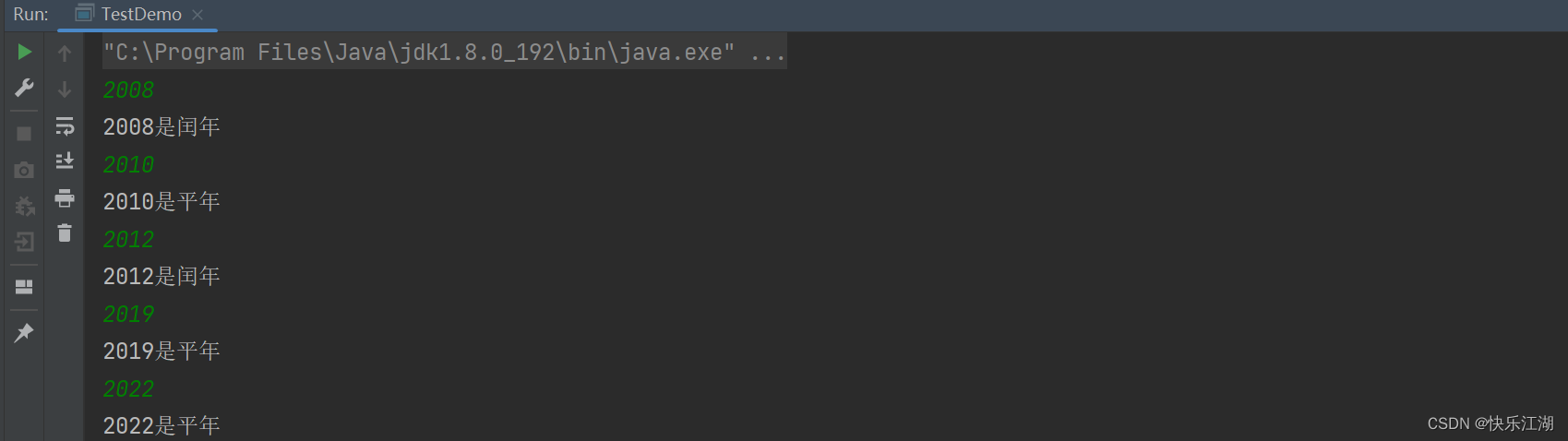
下面是一个判断是否为闰年的例子
- 注意:关于Java中如何从控制台输入后面会说,这里直接使用即可
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//循环输入
while (scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int year = scanner.nextInt();//输入年份
if (year % 100 == 0) {
if (year % 400 == 0) {
System.out.println(year + "是闰年");
} else {
System.out.println(year + "是平年");
}
} else {
if (year % 4 == 0) {
System.out.println(year + "是闰年");
} else {
System.out.println(year + "是平年");
}
}
}
}
}
B:注意事项
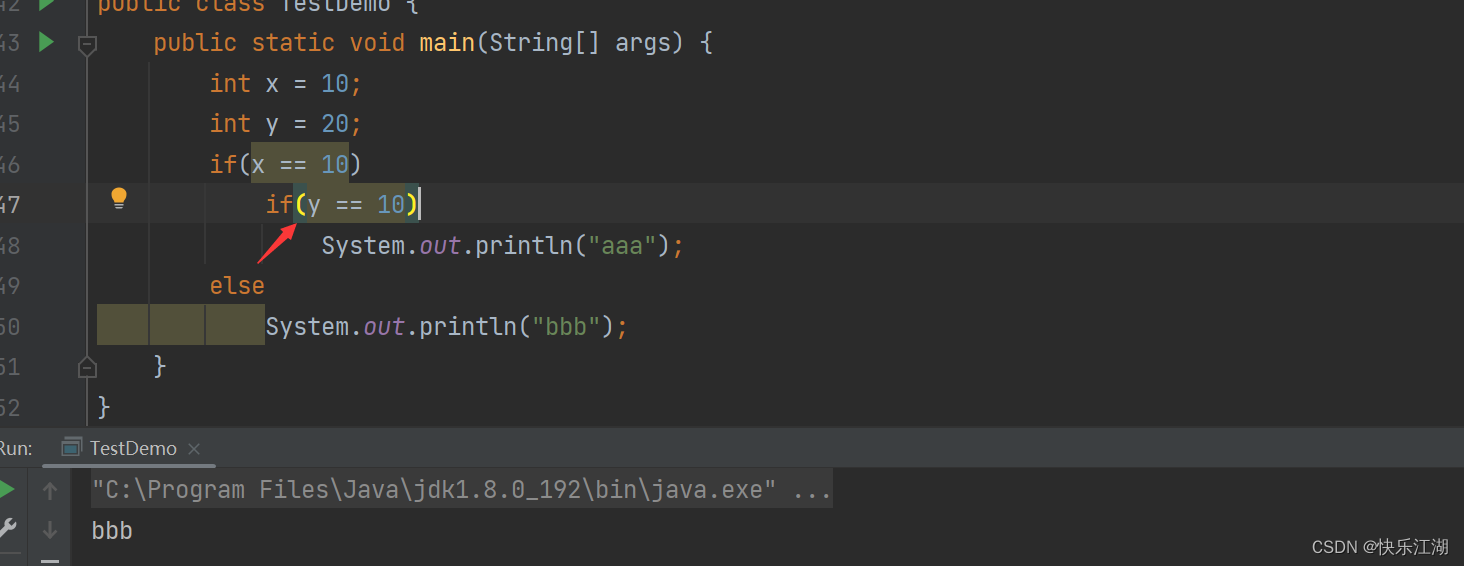
①:使用if语句时推荐下面的风格
- 注意:即便花括号内只有一条语句也请把花括号带上
int x = 10;
if (x == 10) {
// 语句1
} else {
// 语句2
}
②:else匹配时只会匹配离它最近的If
(2)switch语句
A:基本语法
- 具体语法格式不再赘述,和C语言基本一致
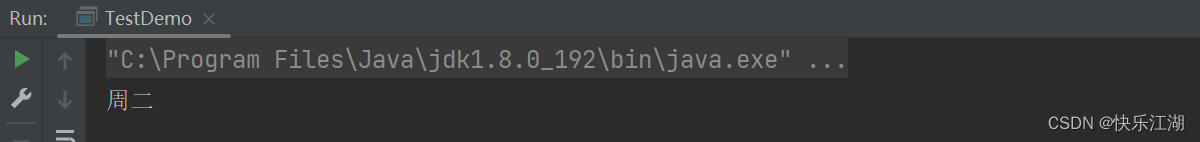
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int day = 2;
switch(day){
case 1:
System.out.println("周一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("周二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("周三");
break;
default:
System.out.println("休息");
break;
}
}
}
B:注意事项
①:多个case后的常量值不可以重复
②:switch括号内不能是以下数据类型
long、float、double、boolean
③:不要遗漏break,否则switch将失去“多分支选择”的效果
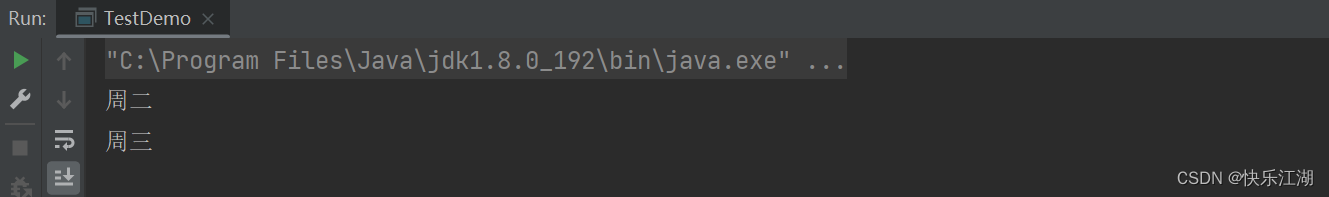
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int day = 2;
switch(day){
case 1:
System.out.println("周一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("周二");
case 3:
System.out.println("周三");
break;
default:
System.out.println("休息");
break;
}
}
}
④:switch无法处理复杂的条件判断语句
二:循环结构
(1)while循环
A:基本语法
- 具体语法格式不再赘述,和C语言基本一致。这里用一些例子熟悉while循环
①:打印1-10
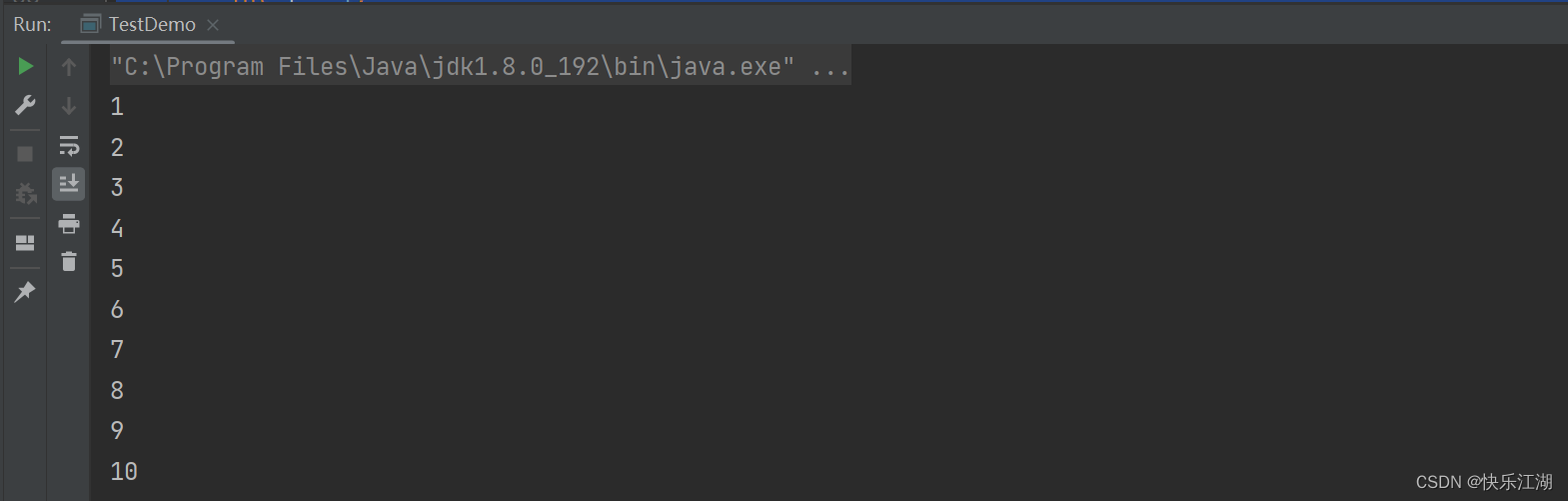
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while(i <= 10){
System.out.println(i++);
}
}
}
②:计算1+2+...+100
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
int sum = 0;
while(i <= 100){
sum+=i++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}

③:计算5!
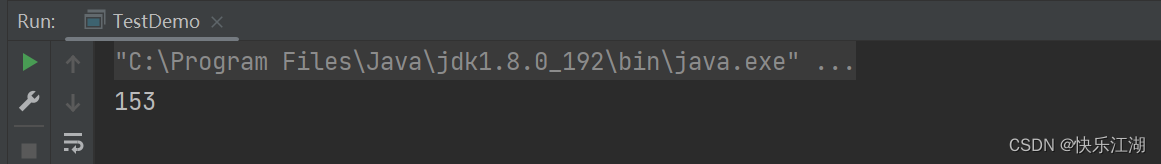
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
int multi = 1;
while(i <= 5){
multi*=i++;
}
System.out.println(multi);
}
}

④:计算1!+2!+3!+4!+5!
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 1;//统计每个阶乘
int ret = 0;
while(num <= 5){
int i = 1;
int multi = 1;
while(i <= num){
multi*=i++;
}
ret+=multi;//累加
num++;
}
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
B:注意事项
①:break
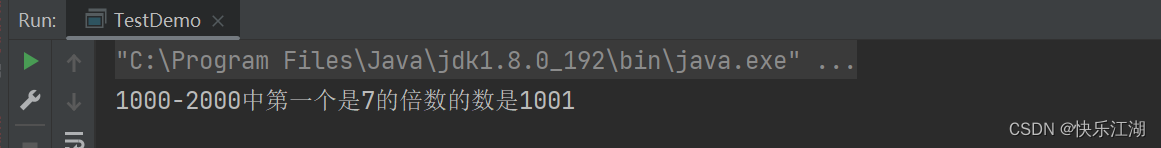
break的作用是让循环提前结束。比如下面的例子
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 1000;
while(num <= 2000){
if(num%7 == 0){
System.out.println("1000-2000中第一个是7的倍数的数是" + num);
break;
}
num++;
}
}
}
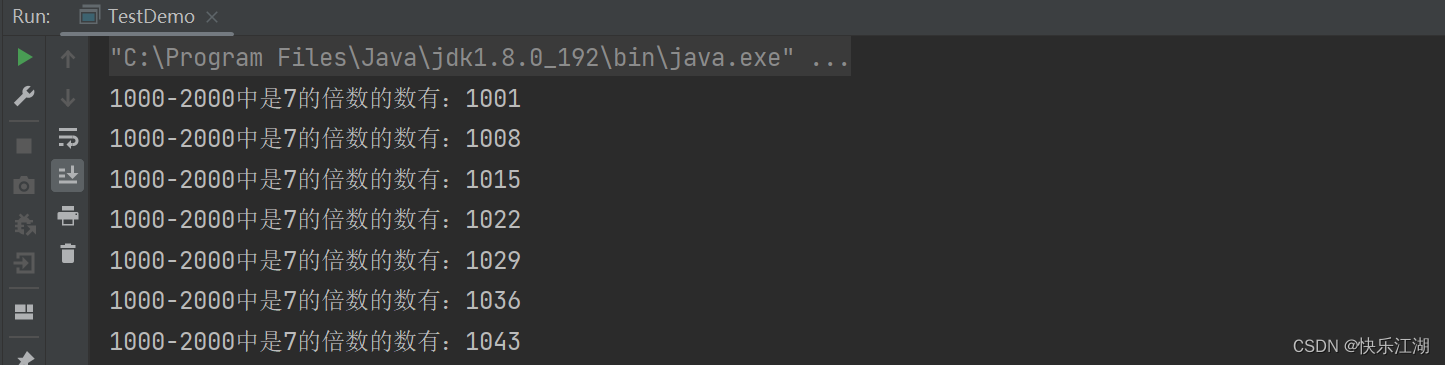
②:continue
continue的作用时跳过本次循环直接进入下一次循环。比如下面的例子
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 1000;
while(num <= 2000){
if(num%7 != 0){
num++;
continue;
}
System.out.println("1000-2000中是7的倍数的数有:" + num + " ");
num++;
}
}
}
(2)for循环
- 具体语法格式不再赘述,和C语言基本一致。这里用一些例子熟悉for循环
①:打印1-10
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
②:计算1+2+…+100
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){
sum+=i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
③:计算5!
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
sum*=i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
④:计算1!+2!+3!+4!+5!
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
int sum = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++){
sum*=j;
}
ret += sum;
}
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
(3)do while循环
- 具体语法格式不再赘述,和C语言基本一致
- do while循环使用场景并不多
int num = 1;
do {
System.out.println(num);
num++;
} while (num <= 10);
三:Java中的输入和输出
(1)输出
Java中向控制台输出信息主要有三种方式
System.out.println(msg);
//输出一一个字符串,带换行
System.out.print(msg);
//输出一个字符串,不带换行
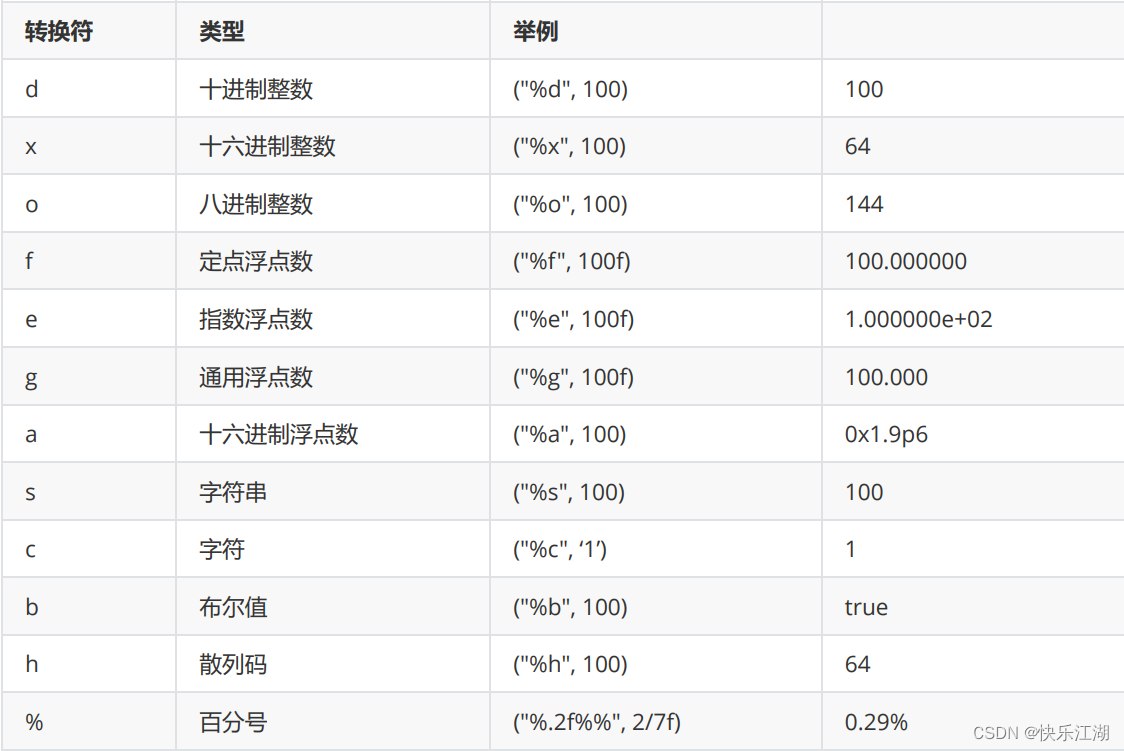
System.out.printf(format, msg); // 格式化输出
其中格式化字符串如下
(2)输入
Java中需要输入信息时需要导入util包
import java.util.Scanner;
导入之后,可以new出一个Scanner对象用于接收信息
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
接着可以调用该Scanner对象的各种方法去接收各种类型的值(注意输入的值的类型一定要匹配)
如果最后不需要输入,记得关闭Scanner
Scanner.close()
这里举一些常见的例子
①:Scanner.nextLine():接收一行信息,使用String接收按下回车时结束输入
Scanner.nextLine():接收一行信息,碰到空格时结束输入
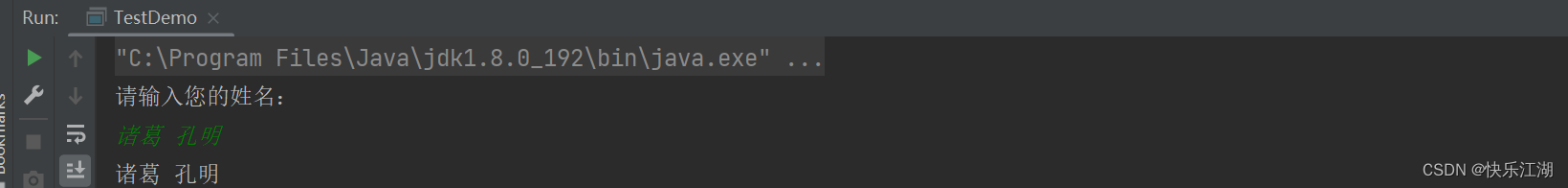
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您的姓名:");
String name =sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(name);
}
}
②:Scanner.nextInt():接收整型
Scanner.nextFloat()/Scanner.nextDouble():接收浮点型
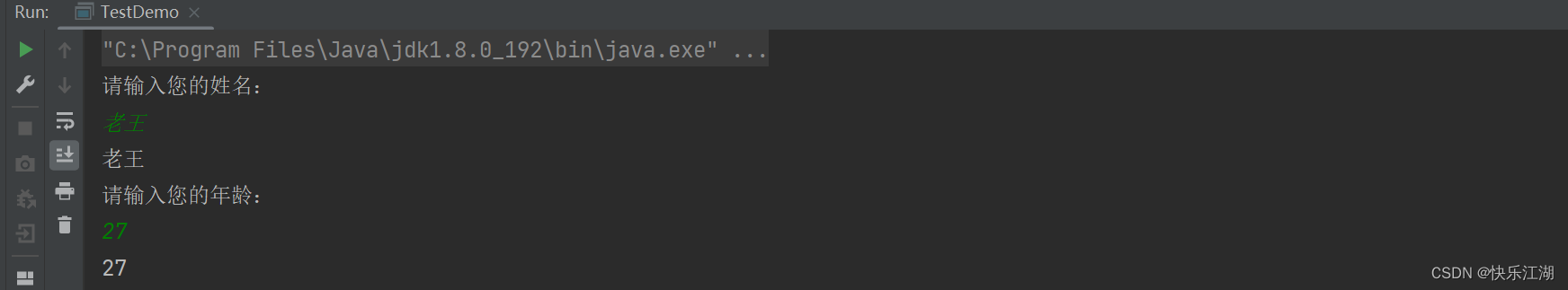
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您的姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("请输入您的年龄:");
int age = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(age);
}
}
③:使用如下方式处理循环输入
- 如下例子用于循环读取10个数字并求它们的和
- 结束输入时按下
ctrl+D
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = 0;
int num = 0;
while(sc.hasNextInt()){
int temp = sc.nextInt();
sum += temp;
num++;
if(num == 10) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
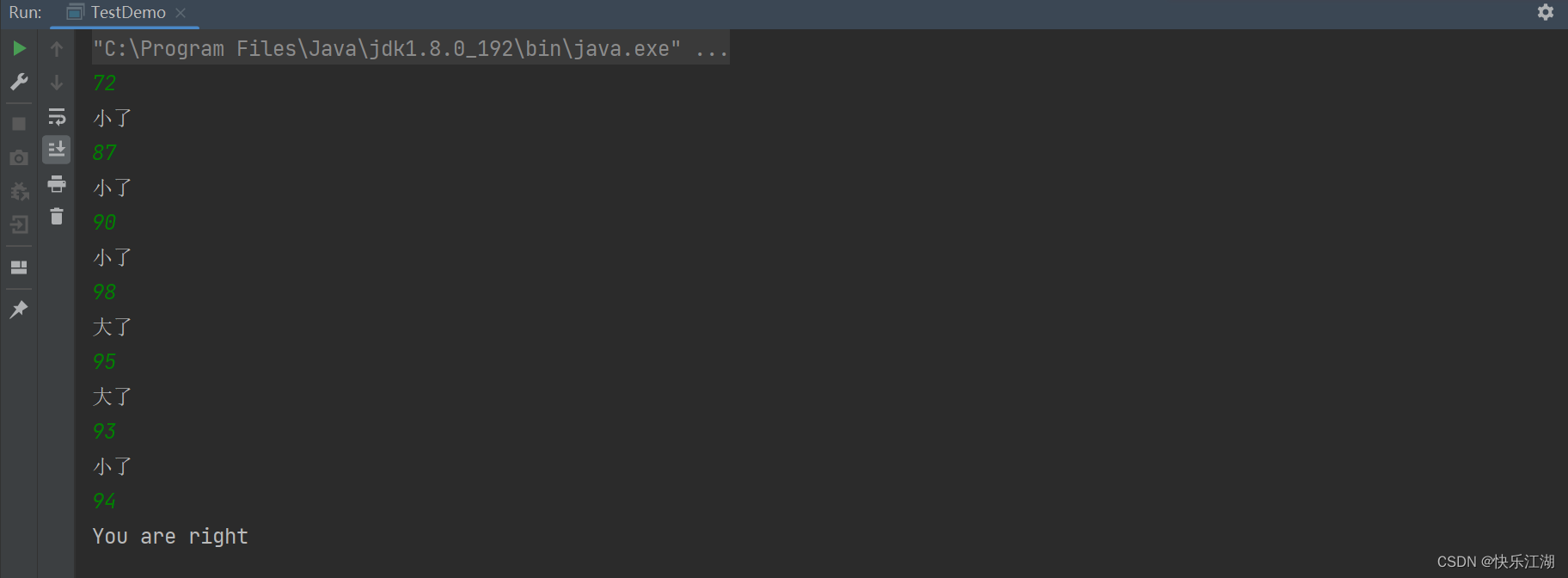
四:猜数字小游戏
结合上面所讲内容,现以一个猜数字的小游戏为例以做巩固练习。游戏规则如下
系统自动生成一个随机整数(1-100), 然后由用户输入一个猜测的数字. 如果输入的数字比该随机数小, 提示 "低 了", 如果输入的数字比该随机数大, 提示 "高了" , 如果输入的数字和随机数相等, 则提示 "猜对了"
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int Guess = random.nextInt(100);
int count = 0;
while(true){
if(count == 10){
break;
}
int num = sc.nextInt();
if(num < Guess){
System.out.println("小了");
}else if(num > Guess){
System.out.println("大了");
}else{
System.out.println("You are right");
break;
}
count++;
}
if(count == 10){
System.out.println("达到10次");
}
sc.close();
}
}


评论区