一:链表相关
(1)链表
链表:为了表示每个数据元素a_{i}与其直接后继数据元素a_{i+1}之间的逻辑关系,对于a_{i}来说,除了存储其本身的信息之外,还需要存储一个指示其后继的信息。我们把存储数据元素的域称之为数据域,把存储直接后继位置的域称之为指针域,这两部分共同组成了一个结点(Node)
(2)链表分类
链表与链表的区别主要体现在以下三个方面
- 单向或双向
- 带头或不带头
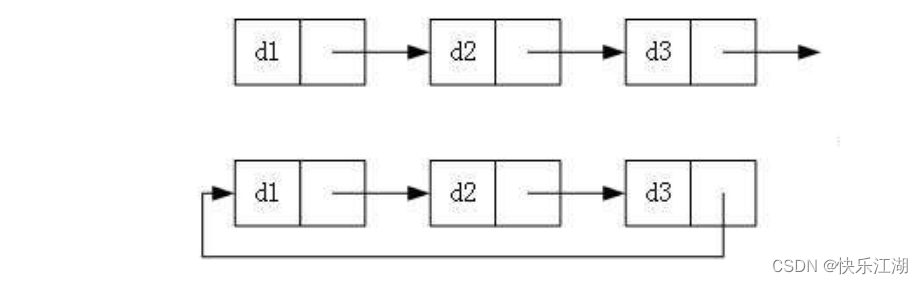
- 循环或非循环
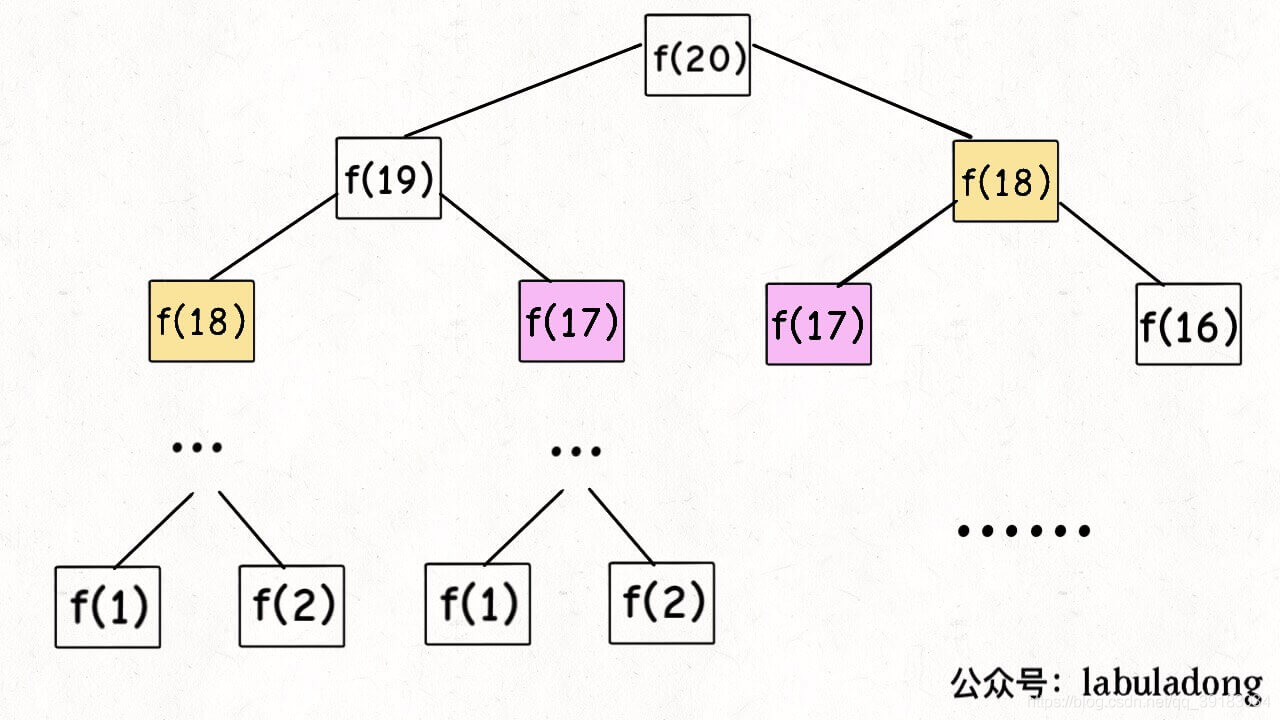
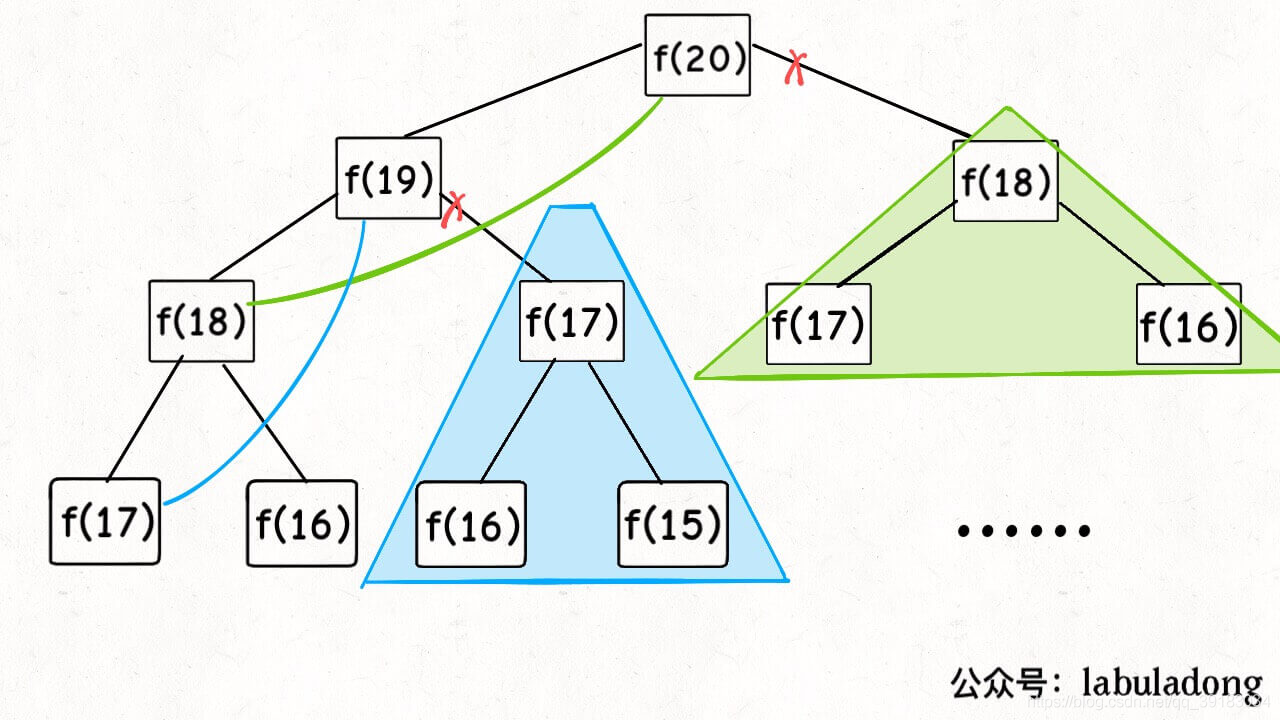
这三种情况搭配下来总共有8种类型的链表,其中我们重点掌握
- 无头单向非循环链表:此种结构一般不会用来存储数据,更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,而且该种结构在面试题中常常出现
- 无头双向循环链表:Java集合框架中的
LinkedList就是一个无头双向循环链表
A:单向或双向
单链表:n个结点链接成一个链表,即为线性表(a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{n})的链式存储结构,由于此链表的每个结点只包含一个指针域,因此称之为单链表
双链表:双链表在单链表的基础上再增加一个指针域,用于指向它的前驱结点
B:带头和不带头
头指针:我们把存储链表中第一个结点位置的指针叫做头指针,常常称之为Head,这个Head相当于是整个链表的龙头,如果头指针丢了,整个链表也就丢了。其中链表最后一个指针指向NULL
头结点:整个链表中的每个结点由数据域+指针域构成,而头指针却好像有点奇怪,因为它没有“实体”,这样做不利于链表统一操作。所以会在单链表的第一个结点前(实际存储有效数据的那个结点)设立一个结点,这个节点指针域装载的就是头指针,但是其数据域不存储任何信息
C:循环和非循环
二:单链表实现
(1)重点说明头插法和尾插法建立单链表
A:尾插法
假设有一个数组,用这些数据以尾插建立单链表
int arr[]={2,12,35,7,344,563,456,234,2346,7}
void CreateListTail(LinkList& L,,int* arr,int n,DataType e)
//arr用于接受数组
//n表示数组长度
{
LNode* p,r;//使用一个指针r始终指向链表最后一个结点
int i;
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode))
r=L;//此时头结点就是最后一个结点
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
p->data=arr[i];
r->next=p;
r=p;//r始终指向尾节点
}
r->next=NULL;//最后指向空,代表链表结束
}
其中最重要的就是r->next=p,r=p

B:头插法
假设有一个数组,用这些数据以头插建立单链表
int arr[]={2,12,35,7,344,563,456,234,2346,7}
void CreatListHead(LinkList& L,int* arr,int n,DataType e)
//arr用于接受数组
//n表示数组长度
{
LNode* p;
int i;
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
L->next=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p=(LNode*)mallco(sizoef(LNode));
p->data=arr[i];
p->next=L->next;//新插入的结点一定要使其处于第一个结点位置
L->next=p;
}
}
其中最重要的就是p->next=L->next、L->next=p
(2)代码实现
package MyLinkedList;
import card.IndexNottLegelException;
public class MySingleList {
//结点定义
static class Node{
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node head;//头结点引用
//构造函数
public MySingleList(){
this.head = null;
}
//检查位置是否合法
private void checkIndex(int index){
if(index < 0 || index > this.size()){
throw new IndexNottLegelException("非法位置");
}
}
//找寻前置结点(依靠位置)
private Node findIndexSubOfOne(int index){
Node cur = head;
while(index-1 != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//找寻前置结点(依靠关键字)
private Node findIndexPreOfOne(int key){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.next.val == key){
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
//打印单链表
public void display(){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val + " -> ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//返回单链表长度
public int size(){
int count = 0;
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
count ++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
//查找该链表是否存在key这个结点
public boolean contains(int key){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//头插法建立单链表
public void creatHead(int data){
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
//尾插法建立单链表
public void creatTail(int data){
Node node = new Node(data);
if(head == null){
head = node;
}else{
Node cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
//任意位置插入
public void addIndex(int index, int data){
checkIndex(index);
if(index == 0){
//等价于头插
this.creatHead(data);
return;
}
if(index == this.size()){
//等价于尾插
this.creatTail(data);
return;
}
//非头插、非尾插,且index合法
Node node = new Node(data);
Node cur = findIndexSubOfOne(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
//删除第一次关键字为key结点
public void remove(int key){
//如果head.val == key
if(this.head.val == key){
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
Node cur = findIndexPreOfOne(key);
if(cur == null){return;}
Node del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
//删除所有值为key的结点
public void removeAll(int key){
if(this.head == null) return;
Node cur = this.head.next;
Node prev = this.head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
prev = cur;
cur =cur.next;
}
}
//如果head.val == key
if(this.head.val == key){
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
}
//清空链表
public void clear(){
this.head = null;//连锁销毁
}
}


评论区