专栏目录首页:【专栏必读】Java基础教程和数据结构内容导航和学习说明
一:经典排序算法概述
| 排序方法 | 类别 | 本文 | 时间复杂度(平均/最好/最坏) | 是否稳定 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直接插入排序 | 插入排序 | 跳转 | O\left ( n^{2}\right )/O\left ( n\right )/O\left ( n^{2}\right ) | 是 | O(1) |
| 希尔排序 | 插入排序 | 跳转 | O(n\log n)/O\left ( n^{1.3}\right )/O\left ( n^{2}\right ) | 否 | O(1) |
| 简单选择排序 | 选择排序 | 跳转 | O\left ( n^{2}\right )/O\left ( n^{2}\right )/O\left ( n^{2}\right ) | 否 | O(1) |
| 堆排序 | 选择排序 | 跳转 | O(n\log n)/O(n\log n)/O(n\log n) | 否 | O(1) |
| 冒泡排序 | 交换排序 | 跳转 | O\left ( n^{2}\right )/O\left ( n\right )/O\left ( n^{2}\right ) | 是 | O(1) |
| 快速排序 | 交换排序 | 跳转 | O(n\log n)/O(n\log n)/O\left ( n^{2}\right ) | 否 | O(\log n)~O(n) |
| 归并排序 | 归并排序 | 跳转 | O(n\log n)/O(n\log n)/O(n\log n) | 是 | O(n) |
(1)直接插入排序(点击跳转)
//0相当于哨兵
void InsertSort(int a[],int n){
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
a[0] = a[i];
int j;
for(j=i-1;a[0]<a[j];j--){
a[j+1] = a[j];
}
a[j+1] = a[0];
}
}
(2)希尔排序(点击跳转)
//0相当于哨兵
void ShellSort(int a[],int n){
for(int d=n/2;d>=1;d/=2){ //增量
for(int i=1;i<1+d;i++){ //按照增量分为d个子表
for(int j=i+d;j<=n;j+=d){ //对每个表进行排序
a[0]=a[j];
int k;
for(k=j-d;k>0&&a[0]<a[k];k-=d){ //找到插入位置
a[k+d]=a[k];
}
a[k+d]=a[0];
}
}
}
}
(3)简单选择排序(点击跳转)
//下标从1开始
void SelectSort(int a[],int n){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int tmp=i;
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++){
if(a[j]<a[tmp]){
tmp=j;
}
}
swap(a[tmp],a[i]);
}
}
(4)堆排序(点击跳转)
- 以大顶堆为例(升序)
//将元素k为根的子树进行调整(大根堆)
void HeadAdjust(int a[],int k,int n){
a[0] = a[k];
for(int i=k*2;i<=n;i*=2){
if(i<n&&a[i]<a[i+1]){
i++;
}
if(a[0]>=a[i]) break;
else{
a[k]=a[i];
k=i;
}
}
a[k] = a[0];
}
//建立大根堆
void BuildMaxHeap(int a[],int n){
for(int i=n/2;i>=1;i--){
HeadAdjust(a,i,n);
}
}
//堆排序
void HeapSort(int a[],int n){
BuildMaxHeap(a,n);
for(int i=n;i>1;i--){
swap(a[i],a[1]);
HeadAdjust(a,1,i-1);
}
}
(5)冒泡排序(点击跳转)
//冒泡排序,元素下标从1开始,从后往前冒泡
void BubbleSort1(int a[],int n){
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
bool flag = false;
for(int j=n;j>i;j--){
if(a[j-1]>a[j]){
swap(a[j-1],a[j]);
flag = true;
}
}
if(!flag) return ;
}
}
//冒泡排序,元素下标从1开始,从前往后冒泡
void BubbleSort2(int a[],int n){
for(int j=n;j>1;j--){
bool flag = false;
for(int i=1;i<j;i++){
if(a[i]>a[i+1]){
swap(a[i],a[i+1]);
flag = true;
}
}
if(!flag) return;
}
}
(6)快速排序(点击跳转)
int Partition(int a[],int low,int high){
int pivot = a[low];
while(low<high){
while(low<high&&a[high]>=pivot) high--;
a[low] = a[high];
while(low<high&&a[low]<=pivot) low++;
a[high] = a[low];
}
a[low] = pivot;
return low;
}
//快速排序
void QuickSort(int a[],int low,int high){
if(low<high){
int pivotpos = Partition(a,low,high);
QuickSort(a,low,pivotpos-1);
QuickSort(a,pivotpos+1,high);
}
}
(7)归并排序(点击跳转)
void Merge(int a[],int low,int mid,int high){
for(int i=low;i<=high;i++){
b[i] = a[i];
}
int k=low,i=low,j=mid+1;
while(i<=mid&&j<=high){
if(b[i]<=b[j]){
a[k++] = b[i++];
}else{
a[k++] = b[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid) a[k++] = b[i++];
while(j<=high) a[k++] = b[j++];
}
void MergeSort(int a[],int low,int high){
if(low<high){
int mid = low+high>>1;
MergeSort(a,low,mid);
MergeSort(a,mid+1,high);
Merge(a,low,mid,high);
}
}
二:Java实现
冒泡排序
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
int count=0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
boolean flag=true;
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1-i; j++) {
if (a[j]>a[j+1]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
flag=false;
}
count++;
}
if (flag) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));// [2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
System.out.println("一共比较了:"+count+"次");//一共比较了:95次
}
}
选择排序
import java.util.Arrays;
//选择排序:先定义一个记录最小元素的下标,然后循环一次后面的,找到最小的元素,最后将他放到前面排序好的序列。
public class SelectSort{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
int index=i;//标记第一个为待比较的数
for (int j = i+1; j < a.length; j++) { //然后从后面遍历与第一个数比较
if (a[j]<a[index]) { //如果小,就交换最小值
index=j;//保存最小元素的下标
}
}
//找到最小值后,将最小的值放到第一的位置,进行下一遍循环
int temp=a[index];
a[index]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}
}
插入排序
import java.util.Arrays;
//插入排序:定义一个待插入的数,再定义一个待插入数的前一个数的下标,然后拿待插入数与前面的数组一一比较,最后交换。
public class InsertSort{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { //长度不减1,是因为要留多一个位置方便插入数
//定义待插入的数
int insertValue=a[i];
//找到待插入数的前一个数的下标
int insertIndex=i-1;
while (insertIndex>=0 && insertValue <a[insertIndex]) {//拿a[i]与a[i-1]的前面数组比较
a[insertIndex+1]=a[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
a[insertIndex+1]=insertValue;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}
}
希尔排序
import java.util.Arrays;
//希尔排序:插入排序的升级
public class ShellSort{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
int count=0;//比较次数
for (int gap=a.length / 2; gap > 0; gap = gap / 2) {
//将整个数组分为若干个子数组
for (int i = gap; i < a.length; i++) {
//遍历各组的元素
for (int j = i - gap; j>=0; j=j-gap) {
//交换元素
if (a[j]>a[j+gap]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+gap];
a[j+gap]=temp;
count++;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);//16
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}
}
快速排序
import java.util.Arrays;
//快速排序:冒泡排序的升华版
public class QuickSort{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int a[]={50,1,12,2};
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
quicksort(a,0,a.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void quicksort(int[] a, int low, int high) {
int i,j;
if (low>high) {
return;
}
i=low;
j=high;
int temp=a[low];//基准位,low=length时,会报异常,java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4 ,所以必须在if判断后面,就跳出方法。
while(i<j){
//先从右边开始往左递减,找到比temp小的值才停止
while ( temp<=a[j] && i<j) {
j--;
}
//再看左边开始往右递增,找到比temp大的值才停止
while ( temp>=a[i] && i<j) {
i++;
}
//满足 i<j 就交换,继续循环while(i<j)
if (i<j) {
int t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
}
//最后将基准位跟 a[i]与a[j]相等的位置,进行交换,此时i=j
a[low]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
//左递归
quicksort(a, low, j-1);
//右递归
quicksort(a, j+1, high);
}
}
归并排序
import java.util.Arrays;
//归并排序
public class MergeSort{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
//int a[]={5,2,4,7,1,3,2,2};
int temp[]=new int[a.length];
mergesort(a,0,a.length-1,temp);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void mergesort(int[] a, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
//分解
if (left<right) {
int mid=(left+right)/2;
//向左递归进行分解
mergesort(a, left, mid, temp);
//向右递归进行分解
mergesort(a, mid+1, right, temp);
//每分解一次便合并一次
merge(a,left,right,mid,temp);
}
}
/**
*
* @param a 待排序的数组
* @param left 左边有序序列的初始索引
* @param right 右边有序序列的初始索引
* @param mid 中间索引
* @param temp 做中转的数组
*/
private static void merge(int[] a, int left, int right, int mid, int[] temp) {
int i=left; //初始i,左边有序序列的初始索引
int j=mid+1;//初始化j,右边有序序列的初始索引(右边有序序列的初始位置即中间位置的后一位置)
int t=0;//指向temp数组的当前索引,初始为0
//先把左右两边的数据(已经有序)按规则填充到temp数组
//直到左右两边的有序序列,有一边处理完成为止
while (i<=mid && j<=right) {
//如果左边有序序列的当前元素小于或等于右边的有序序列的当前元素,就将左边的元素填充到temp数组中
if (a[i]<=a[j]) {
temp[t]=a[i];
t++;//索引向后移
i++;//i后移
}else {
//反之,将右边有序序列的当前元素填充到temp数组中
temp[t]=a[j];
t++;//索引向后移
j++;//j后移
}
}
//把剩余数据的一边的元素填充到temp中
while (i<=mid) {
//此时说明左边序列还有剩余元素
//全部填充到temp数组
temp[t]=a[i];
t++;
i++;
}
while (j<=right) {
//此时说明左边序列还有剩余元素
//全部填充到temp数组
temp[t]=a[j];
t++;
j++;
}
//将temp数组的元素复制到原数组
t=0;
int tempLeft=left;
while (tempLeft<=right) {
a[tempLeft]=temp[t];
t++;
tempLeft++;
}
}
}
堆排序
public class Heap_Sort{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
//构建堆
buildHeap(arr,length);
for ( int i = length - 1; i > 0; i-- ) {
//将堆顶元素与末位元素调换
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
//数组长度-1 隐藏堆尾元素
length--;
//将堆顶元素下沉 目的是将最大的元素浮到堆顶来
sink(arr, 0,length);
}
}
private static void buildHeap(int[] arr, int length) {
for (int i = length / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
sink(arr,i, length);
}
}
private static void sink(int[] arr, int index, int length) {
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;//左子节点下标
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;//右子节点下标
int present = index;//要调整的节点下标
//下沉左边
if (leftChild < length && arr[leftChild] > arr[present]) {
present = leftChild;
}
//下沉右边
if (rightChild < length && arr[rightChild] > arr[present]) {
present = rightChild;
}
//如果下标不相等 证明调换过了
if (present != index) {
//交换值
int temp = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[present];
arr[present] = temp;
//继续下沉
sink(arr, present, length);
}
}
}
三:Collections.sort
Collections.sort:Collections类中的sort方法可以实现List接口的集合进行排序,不过特别注意,在对对象比较时需要实现其Comparator接口,并重写compare方法
如下是对普通数据进行比较
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
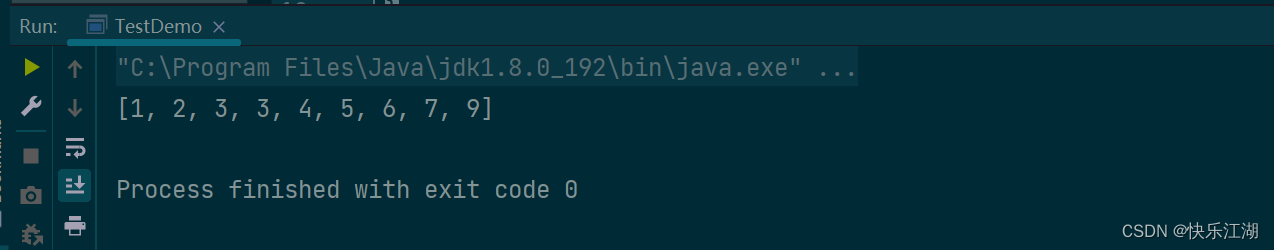
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] testNum = {4, 2, 6, 1, 7, 9, 3, 3, 5};
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(testNum);
Collections.sort(integers);
System.out.println(integers);
}
}
如下是对对象进行比较
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Book {
public String name;
public double price;
public int year;
public Book(String name, double price, int year) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.year = year;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "【name:" + this.name + ";price:" + this.price + ":year:" + this.year + "】\n" ;
}
}
//按照价格升序排序比较器
class BookComparatorByPriceAscend implements Comparator<Book> {
@Override
public int compare(Book o1, Book o2){
if(o1 == o2){
return 0;
}
if(o1 == null){
return -1;
}
if(o2 == null){
return 1;
}
if((o1.price - o2.price) < 0){
return -1;
}else if((o1.price - o2.price) == 0){
return 0;
}else{
return 1;
}
}
}
//按照年份降序排序比较器
class BookComparatorByYearDescend implements Comparator<Book> {
@Override
public int compare(Book o1, Book o2){
if(o1 == o2){
return 0;
}
if(o1 == null){
return -1;
}
if(o2 == null){
return 1;
}
if((o1.year - o2.year) < 0){
return 1;
}else if((o1.price - o2.price) == 0){
return 0;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Book> books = new ArrayList<>();
books.add(new Book("水浒传",78,2200));
books.add(new Book("西游记", 88, 1999));
books.add(new Book("红楼梦",28,1820));
books.add(new Book("三国演义",68,1999));
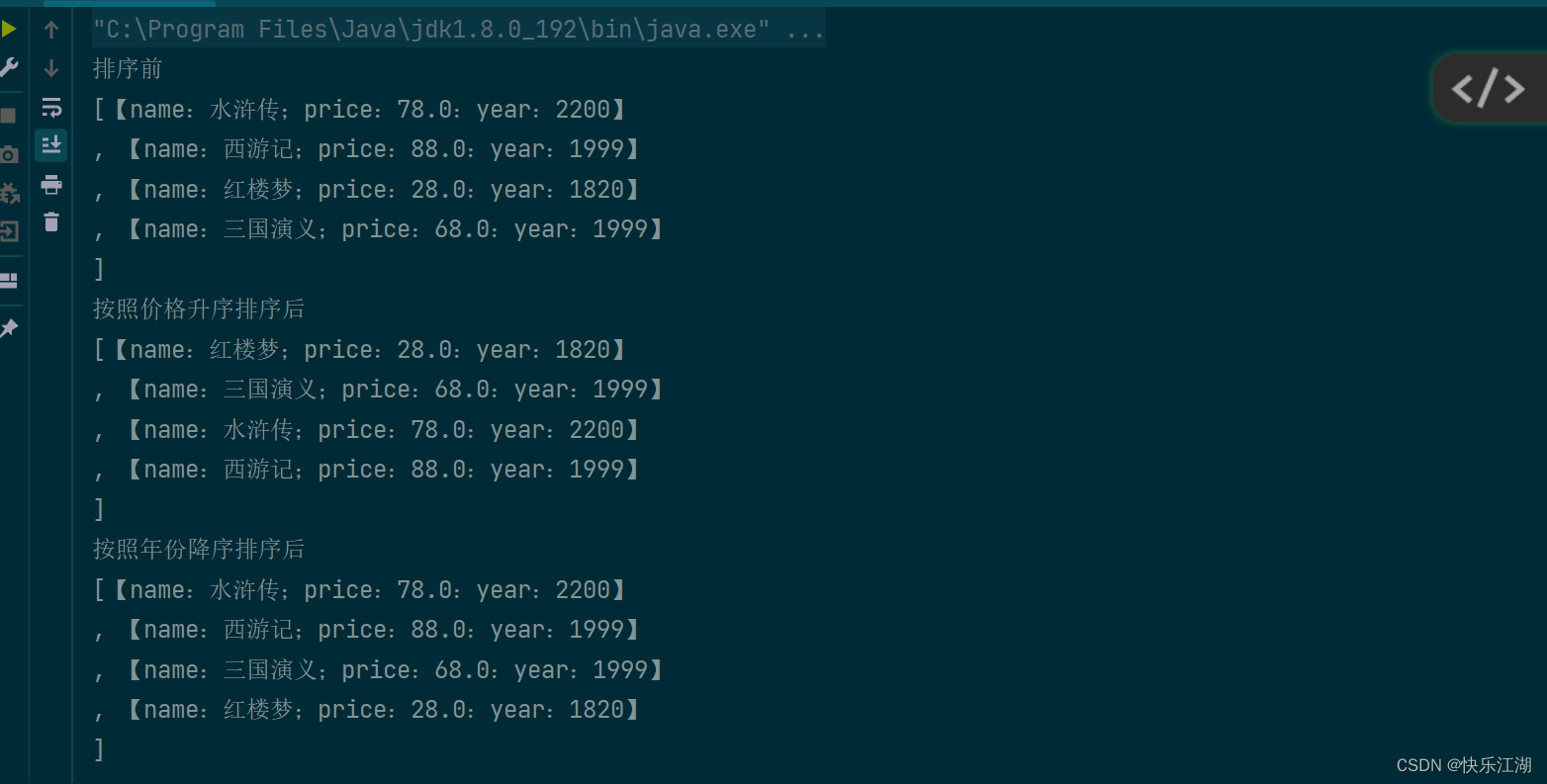
System.out.println("排序前");
System.out.println(books);
Collections.sort(books, new BookComparatorByPriceAscend());
System.out.println("按照价格升序排序后");
System.out.println(books);
Collections.sort(books, new BookComparatorByYearDescend());
System.out.println("按照年份降序排序后");
System.out.println(books);
}
}


评论区